Movements in Migration + Money
Where people go, money flows.
Migration patterns reveal more than statistics. They offer a lens through which leaders can comprehend the intricate dynamics of global labor markets, economic leverage, climate challenges, and demographic transformations. For globally ambitious leaders, recognizing and acting on these insights can drive strategic growth and innovation to form a competitive edge.
The Economic Power of Migration
Migration is a human story and it is also a driver of economic growth.
Remittances represent money that migrant workers send back to their families and communities in their home countries. Unlike foreign aid or investment, remittances go directly to individuals, providing immediate support for basic needs like food, healthcare, education, and housing.
In 2022, migrant remittances surged to US$831 billion, up from US$128 billion in 2000, surpassing foreign direct investment as a key contributor to GDP in a number of low- and middle-income economies. For countries like India, Mexico, and the Philippines, these financial flows make important economic contributions (IOM, 2024).
At the same time, migrant workers play an essential role in international labour markets, particularly in regions experiencing acute demand. For example, in the Arab states, migrant workers comprise over 40% of the workforce (EPW, 2024). Globally, 169 million migrants contribute their skills and labour, filling gaps across sectors from technology to agriculture.
Emerging Trends in Migration Flows
While migration has grown steadily – rising from 84 million in 1970 to 281 million in 2020 – it is not following traditional patterns. The narrative of migration moving from poorer to richer nations is evolving. High-income countries like Canada, Australia, and the UAE are seeing sharp increases in immigrant populations. Much of this movement occurs between economically developed nations as they compete for skilled workers, students, and investors (OECD, 2024).
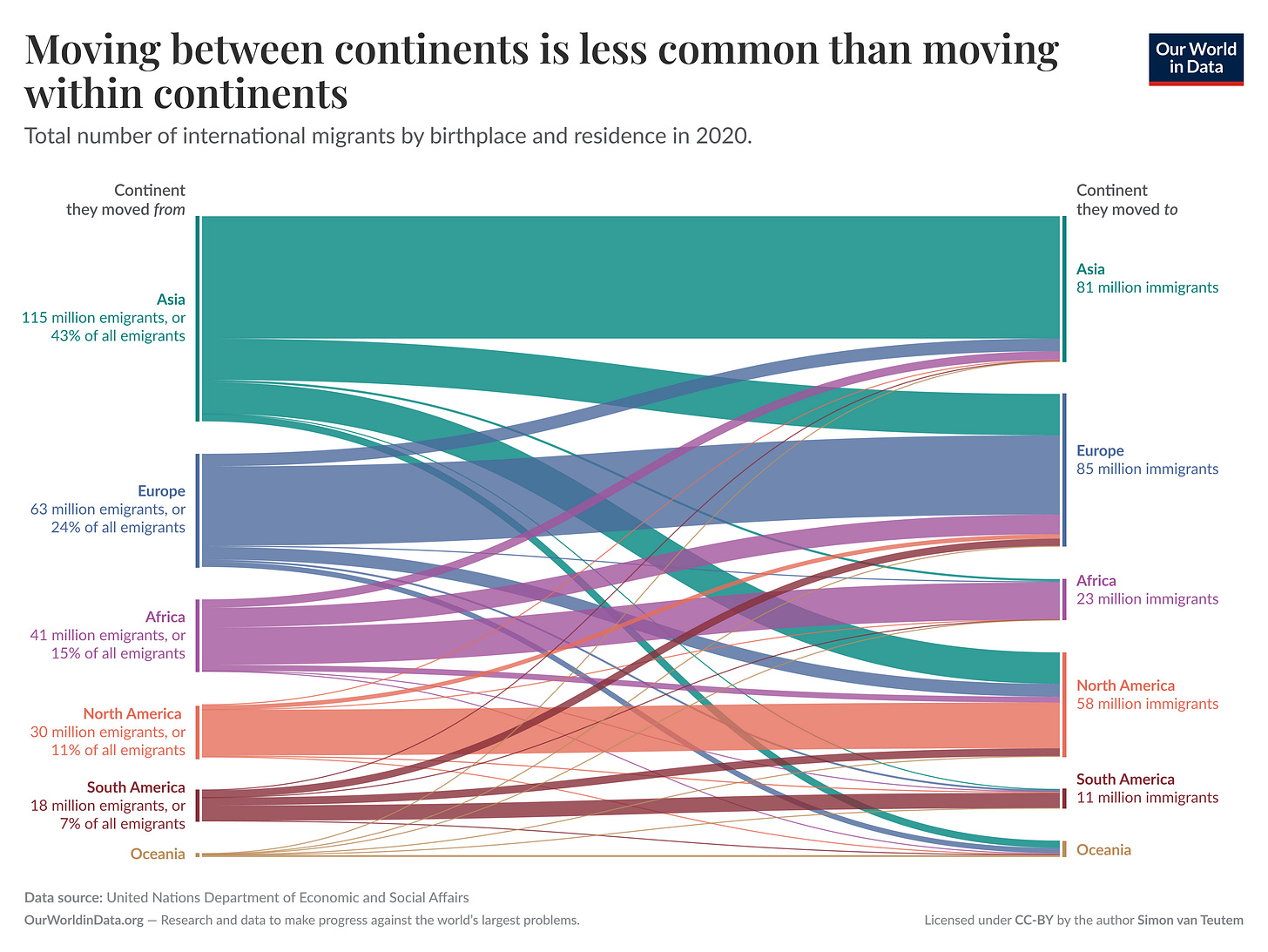
Most typically migrants don’t go far - the below graph illustrates that moving between continents is much less common than moving to another country within the same region.
Gig Growth
Gig economy opportunities are also playing a transformative role, particularly in smaller, digitally advanced nations like Estonia. Through innovative visa programs and digital residency initiatives, Estonia has positioned itself as a hub for global gig workers. Its e-Residency program enables freelancers and entrepreneurs to operate borderless businesses, connecting them to global markets and creating economic opportunities for migrant workers. To date Estonia has attracted over 119,000 e-residents from 170+ countries all around the world, with €15 billion combined revenue of e-resident companies (Estonian e-Residency, 2024).
Mobility Under Pressure
Across the world, migration faces increasing barriers. Restrictive immigration policies in leading destinations such as Australia, Canada, and the UK are creating headwinds for international students and workers. Concerns over housing affordability and rising living costs are key drivers of this shift (ICEF, 2024).
Forced migration presents an even more urgent challenge. By the end of 2023, over 117 million people were displaced due to conflict, climate change, and economic instability (UNHCR, 2023).
Climate Change as a Migration Driver
Climate change is reshaping migration patterns. From rising sea levels displacing island communities to drought-driven food insecurity pushing rural populations to urban centres, environmental crises are accelerating human mobility. For instance, regions across Africa and South Asia are experiencing significant climate-induced displacement (IOM, 2024).
Shifts in Gender and Demographics
Demographic changes within migration reveal further nuances. Over the past 25 years, the percentage of children migrating has dropped from 16% to 10%. While male migration has grown slightly, women still dominate flows in many developed countries, such as Canada and the United States (EPW, 2024).
Startups Thriving by Serving Migrant Communities
A number businesses and startups have emerged to address the unique needs of migrant communities, demonstrating both impact and opportunity, including:
Remitly (USA)
Focus: Digital remittance services for migrants to send money to their home countries.
Impact: Remitly simplifies and reduces costs for sending remittances, addressing a critical US$831 billion market that boosts financial inclusion globally.Kheyti (India)
Focus: Agricultural solutions for small-scale farmers, including internal migrants.
Impact: Kheyti’s “Greenhouse-in-a-box” enables migrant farmers to adapt to climate challenges, improving yields and incomes.Workana (Argentina)
Focus: Freelance work platform connecting skilled migrant workers with international employers.
Impact: Migrants access global digital jobs, bypassing geographical and economic barriers.Migracode (Spain)
Focus: Coding bootcamps and digital skills training for migrants and refugees.
Impact: Migrants gain employable tech skills, accessing opportunities in Europe’s IT sector.
These businesses highlight how digital connectivity and innovative solutions can scale and serve migrant communities while unlocking economic value, securing a share of a growing market, and fostering sustainable development.
Leading with Insight and Action
Migration patterns are not static; they reflect the pulse of a changing world. Where people go, money flows - migration impacts economic growth and financial interconnections worldwide. Leaders who understand these shifts can better navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and build strategies that contribute to long-term success.
These migration and money patterns remind us:
When we see the bigger picture, we can play a bigger game.
The world, and its people, shift.
Today’s shifts shape the problems leaders will solve tomorrow.
By recognizing the economic, demographic, and environmental forces at play, leaders can leverage migration patterns from a complex challenge into a strategic opportunity for global development, innovation, and inclusive growth.
The future belongs to those who leverage global shifts to shape action.